
Qt for Android provides a complete solution to develop, build, and package your applications for Android. Most of these tasks, especially packaging and deployment, are handled by Qt Creator, providing a rich developer experience.
Every time you run the application using Qt Creator, an Android Application Package (APK) is created and deployed onto the target of your choice (device or emulator). With a few minor changes to packaging settings, you can publish your application on Google Play.
Once your app has been developed and you want to move forward to publish it to Google Play, follow these instructions to create an .apk or .aab that can go live on
Google Play:
Release Build.AndroidManifest.xml, which is the main file of concern here.AndroidManifest.xml:
android:label under the manifest's application section.See Qt Android Manifest File Configuration for more information.
minimum and target SDK versions according to your app's needs. This can be done using the CMake properties QT_ANDROID_TARGET_SDK_VERSION and QT_ANDROID_MIN_SDK_VERSION. Or for
qmake ANDROID_TARGET_SDK_VERSION ANDROID_MIN_SDK_VERSION.
Note: As before with Qt 5.15, you can specify these settings in the AndroidManifest.xml. Be aware that the CMake and qmake properties mentioned above will override these if set there.
See Android: App Versioning for more information on setting these in build.gradle.
.apk package at:
<build_path>/android-build/build/outputs/apk/release/android-build-release.apk
Note: In Qt Creator, select Projects > Build > Build Steps > Build Android APK > Open
package location after build to build the application's .apk and open the directory containing the package.
.aab file, then locate the package at:
<build_path>/android-build/build/outputs/bundle/release/android-build-release.aab
Log into the Google Play Developer Console and upload the .aab files, along with a description and screen captures resembling the usage of your
application.
Uploading one .aab with all the supported architectures is enough for Qt versions that support building a multi-ABI bundle. Qt 6.8 supports building multi-ABI bundles with only with CMake.
For more information, see QT_ANDROID_ABIS.
However, publishing your app requires additional steps for Qt versions that don't have the multi-ABI build support. qmake builds in Qt 6.8 fall into this category.
To publish your app that is built using a single ABI kit, you need to make sure that each ABI uses a different internal version code. The version code is an internal non-public identifier for your app's release. Build each one of the architectures you want to support and set a different version code for each ABI. This can be done as follows for qmake:
ANDROID_VERSION_CODE = <unique_version>
The app developer can use a specific scheme for the version code. For example, the code could have chunks for the platform, the ABI, and the actual version. Then, a sample scheme would be <Platform><ABI><AppVersion>:
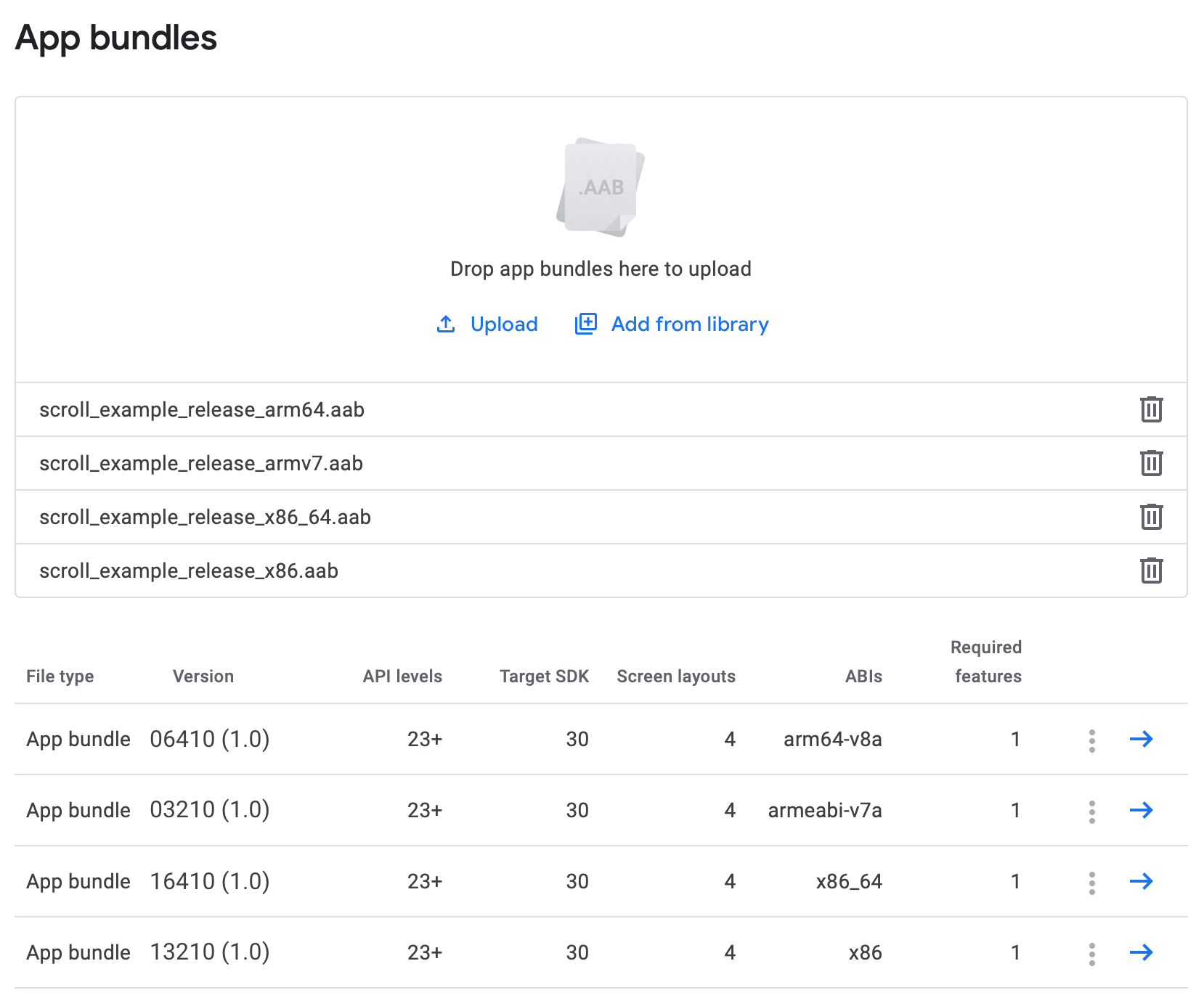
The resulting version code for release 1.0 for arm64-v8a ABI, would be 16410.
For more information, see Google's documentation on app versioning.
The following screenshot shows an example of an app targeting 4 ABIs, while each package uses a unique version code, which is different from the version name that is the public version string.
See also Deploying an Application on Android.