
The QCameraDevice class provides general information about camera devices. More...
| Header: | #include <QCameraDevice> |
| CMake: | find_package(Qt6 REQUIRED COMPONENTS Multimedia)target_link_libraries(mytarget PRIVATE Qt6::Multimedia) |
| qmake: | QT += multimedia |
| enum | Position { UnspecifiedPosition, BackFace, FrontFace } |
|
|
| QCameraDevice() | |
| QCameraDevice(const QCameraDevice &other) | |
| ~QCameraDevice() | |
| QtVideo::Rotation | correctionAngle() const |
| QString | description() const |
| QByteArray | id() const |
| bool | isDefault() const |
| bool | isNull() const |
| QList<QSize> | photoResolutions() const |
| QCameraDevice::Position | position() const |
| QList<QCameraFormat> | videoFormats() const |
| bool | operator!=(const QCameraDevice &other) const |
| QCameraDevice & | operator=(const QCameraDevice &other) |
| bool | operator==(const QCameraDevice &other) const |
QCameraDevice represents a physical camera device and its properties.
You can discover what cameras are available on a system using the availableCameras() and defaultCamera() functions. These are contained within QtMultimedia::MediaDevices.
The QCameraDevice instance retains its properties throughout its lifetime, even if the corresponding physical device is disconnected or its settings are modified. To keep track of updated properties, the user should load new instances of QCameraDevice from QMediaDevices when the relevant signals are fired.
This example prints the name of all available cameras:
const QList<QCameraDevice> cameras = QMediaDevices::videoInputs(); for (const QCameraDevice &cameraDevice : cameras) qDebug() << cameraDevice.description();
A QCameraDevice can be used to construct a QCamera. The following example instantiates a QCamera whose camera device is named mycamera:
const QList<QCameraDevice> cameras = QMediaDevices::videoInputs(); for (const QCameraDevice &cameraDevice : cameras) { if (cameraDevice.description() == "mycamera") camera = new QCamera(cameraDevice); }
You can also use QCameraDevice to get general information about a camera device such as description and physical position on the system.
QCamera myCamera; QCameraDevice cameraDevice = camera->cameraDevice(); if (cameraDevice.position() == QCameraDevice::FrontFace) qDebug() << "The camera is on the front face of the hardware system."; else if (cameraDevice.position() == QCameraDevice::BackFace) qDebug() << "The camera is on the back face of the hardware system.";
See also QCamera.
This enum specifies the physical position of the camera on the system hardware.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QCameraDevice::UnspecifiedPosition |
0 |
The camera position is unspecified or unknown. |
QCameraDevice::BackFace |
1 |
The camera is on the back face of the system hardware. For example on a mobile device, it means it is on the opposite side to that of the screen. |
QCameraDevice::FrontFace |
2 |
The camera is on the front face of the system hardware. For example on a mobile device, it means it is on the same side as that of the screen. Front-facing cameras generate video frames with the property QVideoFrame::mirrored set to true. This means that the presentation of these frames is flipped around the vertical axis to display the video output as a
mirror, whereas recording only considers the transformations of the surface specified in QVideoFrame::surfaceFormat.
|
See also position().
[read-only, since 6.7] correctionAngle : const QtVideo::RotationReturns the rotation angle needed to compensate for the physical camera rotation of the camera compared to its native orientation. In other words, the property represents the clockwise angle through which the output image needs to be rotated to be upright on the device screen in its native orientation. Since correctionAngle is relative to the native orientation, this value does not change with altering the device orientation (portrait/landscape). The correction angle may be non-zero mostly on Android, where native and camera orientations are defined by the manufacturer.
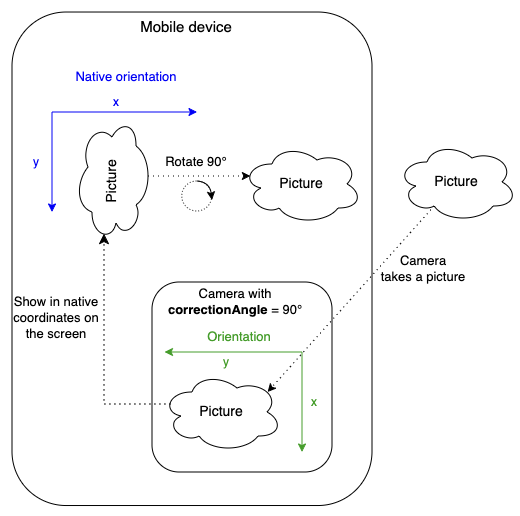
This property was introduced in Qt 6.7.
Access functions:
| QtVideo::Rotation | correctionAngle() const |
[read-only] description : const QStringReturns the human-readable description of the camera.
Use this string to present the device to the user.
Access functions:
| QString | description() const |
[read-only] id : const QByteArrayReturns the device id of the camera
This is a unique ID to identify the camera and may not be human-readable.
Access functions:
| QByteArray | id() const |
[read-only] isDefault : const boolReturns true if this is the default camera device.
Access functions:
| bool | isDefault() const |
[read-only] position : const PositionReturns the physical position of the camera on the hardware system.
Access functions:
| QCameraDevice::Position | position() const |
[read-only] videoFormats : const QList<QCameraFormat>Returns the video formats supported by the camera.
Access functions:
| QList<QCameraFormat> | videoFormats() const |
Constructs a null camera device
Constructs a copy of other.
[noexcept] QCameraDevice::~QCameraDevice()Destroys the QCameraDevice.
Returns true if this QCameraDevice is null or invalid.
Returns a list of resolutions that the camera can use to capture still images.
See also QImageCapture.
Returns true if this QCameraDevice is different from other.
Sets the QCameraDevice object to be equal to other.
Returns true if this QCameraDevice is equal to other.